Written By ————
Earlier in this series of articles, we have discussed about the forms of businesses, registered and unregistered, and have discussed in detail about the unregistered business structures. Given the existing understanding on selecting a right business structure, this article will help in narrowing down your approaches while selecting an appropriate business structure for your new and/or existing business in India.
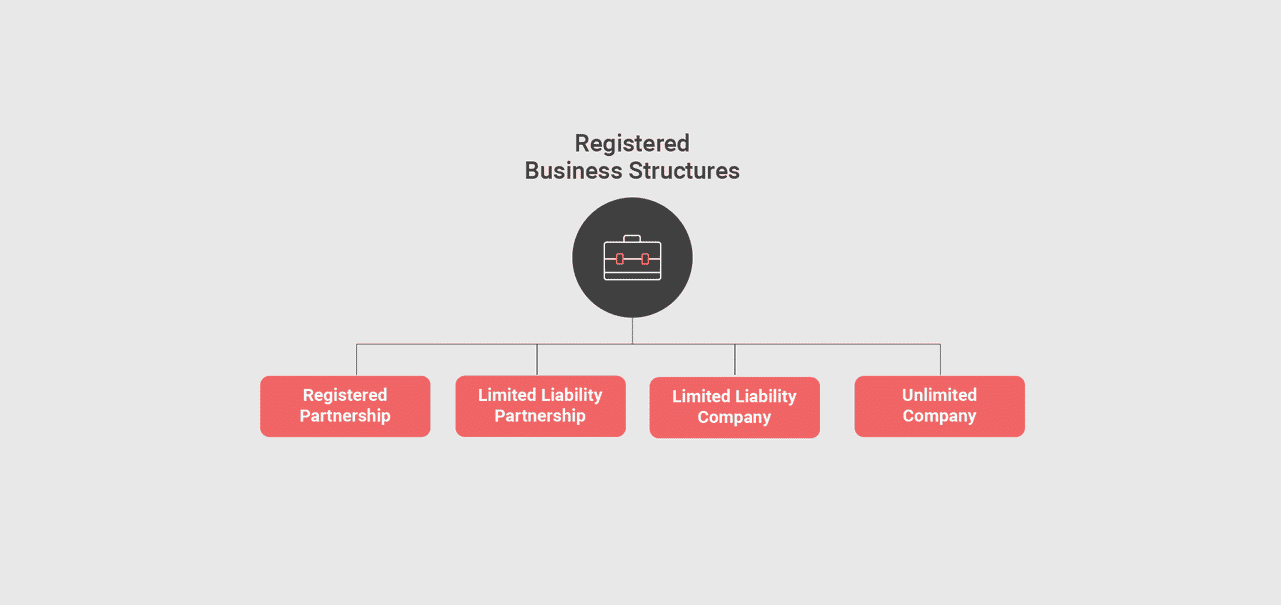
Basis above, we would like to focus your attention on the following registered possible business structures in India for guiding your approach towards the favorable direction and an organized universe:
Different Types Of Registered Business Structures:
Registered business structures, typically referred to as organized business structures, are the complex yet simple form of business structures. Through complex yet simple form of business structures, we mean that such structures may be incorporated through a lengthy process and comes with a complex compliance management as compared to unregistered business structures but once equipped with the understanding about the compliances, such structures can reap million other benefits in long run.
Such business structures are tagged along with more pros than cons which are as follows:
Pros
-
Separate legal entity, except in the case of registered partnerships.
-
Limited Liability in general except in the case of registered partnerships.
-
Approachable and easy access to various government schemes.
-
Additional borrowing capacities.
-
Facility of a corporate veil between the business and the promoters, except in the case of registered partnerships and/or the case of frauds.
Cons
-
Higher degree of compliances.
-
Lengthy registration process.
-
Higher cost of management.
The cons are significantly limited to the associated costs, whether actual or opportunity but the satisfaction of pros can over-power the cons of the registered business structures.
Let us now quickly look at the forms of registered business structures and the necessary structural procedures associated with their creation:
Registered Partnerships
A registered partnership in India is established in accordance with the Indian Partnership Act, 1932 and partnership deed between the partners are governed by the said law along with the Indian Contract Act, 1872. By registered partnerships, we mean that a partnership as an option, can be registered with the Registrar of firms (ROF) through a written partnership deed.
The aforesaid pros and cons are not completely applicable on the registered partnerships. Such structure may be registered but are similar to the unregistered partnerships which was discussed previously.
A partnership deed usually should have the following clauses as the essence clauses:
-
Details of partners like their name, address etc.;
-
Proposed business name;
-
Registered address of business;
-
Duration of Partnership, if applicable;
-
Profit Sharing ratio between the partners along with their respective capital contributions;
-
Admission and Retirement process for the partners;
-
Dissolution process;
-
Dispute resolution clause;
-
Business Procedural clauses;
-
Any other clauses as may be agreed between the partners;
Starting a business with a registered partnerships is comparatively easier and is subject to lesser rules and regulations than any other forms of business. A registered partnership can begin in a few days with almost insignificant costs and can be formed according to the following process:
-
Drafting of a partnership deed;
-
Procuring stamps in the name of the business;
-
Filing of an application for registration with the Registrar of Firms wherein the firm is proposed to be situated along with the payment of fees and duties;
-
Obtaining Registration Certificate;
-
Obtaining Permanent Account Number (PAN), Tax Deduction and Collection Account Number (TAN);
-
Opening a bank account in the name of the business;
-
Any other registrations shall be subject to the objects of the business.
Limited Liability Partnerships
A Limited Liability Partnership (‘LLP’) is a partnership structure of two or more partners with a limited liability. An LLP is created and governed in accordance with the Limited Liability Partnership Act, 2008 read with the Limited Liability Partnership Rules, 2009. An LLP, as the name suggest, has corporation and partnership elements, and has a separate legal existence which is different from its partners.
An LLP like the partnerships, is governed by the provisions of the LLP Agreement in addition to the aforesaid act and rules. Comparatively, it comes with a lower level of compliances, lower costs with an easy day to day operations.
Starting your venture through an LLP is comparatively easier and hassle-free. Many budding entrepreneurs in India considers this as a boon for them to begin their business through an LLP. The following are some of the features of an LLP:
-
Limited Liability of the partners, except in the cases when the partners are found guilty of frauds, misrepresentations etc.
-
An LLP has a separate legal existence different from its partners i.e, capable to enter into contracts and arrangements and/or capable of holding assets and liabilities in its own name.
-
There is no limit on the total number of partners.
-
There is no requirement of the minimum capital contribution.
Talking about the negatives, an LLP cannot raise funds through equity and has always been less lucrative while raising funds from an investor.
The process of incorporating an LLP is altogether an online process wherein the filings are made on the website of the Ministry of Corporate Affairs (‘MCA’). Such process has been briefed below for your reference:
-
E-filing for the reservation of name (optional).
-
E-filing for the incorporation and obtaining the certificate of incorporation.
-
Drafting of an LLP agreement and registration thereof through an e-filing of form.
Limited Liability Company
A Limited Liability Company is a business structure with a legal existence separate from its members and is capable of being survived until perpetuity. A Limited Liability Company in India is created and governed in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013.
A Limited Liability Company can further be categorized into the following type of companies:
-
Private Limited Company
-
Public Limited Company
-
One Person Company
A Limited Liability Company comes with the following Characteristics:
-
A company can be categorized as a legal artificial person which has its own existence in the eyes of laws. Due to its independent legal existence as a person, a company can enter into any contract and/or arrangements with any person, can sue and/or can get sued as a natural person.
-
Limited Liability of Members: As the name suggests, the liability of members of the company are limited in nature. In the event of dissolution and/or liquidation caused by the losses, the member shall be liable to pay up to a committed amount only. However, there are certain exceptions to this characteristic in the cases of fraud, mala fide intentions or any such similar situation.
-
A Limited Liability Company has a perpetual succession i.e., it can never die on its own. Even in case of the death of all the members, a company shall continue to exist through its representatives or heirs.
-
Easy Exits: A member of the company can easily exit from the company through a basic process of transferring the shares of the company to any other individual/ entity.
Besides the aforesaid characteristic of a limited liability company, it comes with numerous pros and a few cons which are as follows:
Pros
-
It is widely recognized business structure throughout the Globe.
-
It facilitates better governance and control over the business activities due to defined procedures and guidelines by law.
-
Fund raising, whether from public or private, is an easier process due to its recognition, defined procedures, and easy exits when the objectives have been achieved.
-
With a bona fide intention, a member can never be forced to pay more than the committed amount of sum in the cases of business failure and/or losses. Thus, it brings a sense of security to the personal assets of the members of the company.
Cons
-
Higher governance brings higher degree of compliances; thus, the compliances are usually higher in any Limited Liability Company.
-
The cost of managing a company is slightly higher.
-
As has been the history and experience, management disputes may create a dead-lock situation. In order to avoid such situation, there can be a requirement of additional and stricter paperwork
Unlimited Company
-
Unlimited Liability Company, as the name suggests, is a form business structure wherein the liability of members is unlimited. It can be categorized as a hybrid of a partnership structure and a limited liability company. Besides the unlimited liability, the members of the company enjoy all the other benefits of a limited liability company.
-
Such form of business structure is a beneficial structure from a point of view of the creditors of the company. The creditors have more chances of recovering their money in the cases of default or otherwise vis-à-vis it is beneficial for the company to convince their creditors and get the credit for running the businesses.
-
An Unlimited Liability Company in India is created and governed in accordance with the provisions of the Companies Act, 2013. Such companies are incorporated through a similar process of incorporating a Limited Liability Company.
Thus, we can say that the aforesaid information about the registered business structures may be enough to make a wise and sound decision before choosing the right structure for your business. However, it is important to weigh all the pros and the cons of any business structure depending upon your vision and upon your long-term goals.
Please note that there may be additional other factors while choosing a business structure. Such factors have not been elaborated in this series of articles like tax rates, government subsidies, locational advantages etc. which should be accounted for while making any decision with respect to choosing any business structure.
Priyank kukreja